35. Vitrification
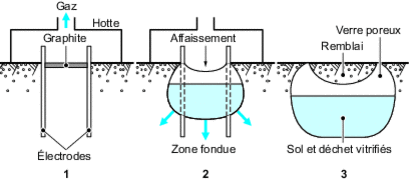
Vitrification is the transformation of soil (the part not saturated with water) by heat into a molten material which, after cooling, becomes a glass encapsulating the pollutants (figure 35 ). The technique is functional but not widely used, as it is costly due to the energy consumption of the process. Vitrification has interesting applications in the case of soils contaminated by metals or certain radio-nuclides. In the end, however, the metals remain in the soil but are immobilized.
Exclusive to subscribers. 97% yet to be discovered!
You do not have access to this resource.
Click here to request your free trial access!
Already subscribed? Log in!

The Ultimate Scientific and Technical Reference
This article is included in
Public works and infrastructure
This offer includes:
Knowledge Base
Updated and enriched with articles validated by our scientific committees
Services
A set of exclusive tools to complement the resources
Practical Path
Operational and didactic, to guarantee the acquisition of transversal skills
Doc & Quiz
Interactive articles with quizzes, for constructive reading
Vitrification
References
Exclusive to subscribers. 97% yet to be discovered!
You do not have access to this resource.
Click here to request your free trial access!
Already subscribed? Log in!

The Ultimate Scientific and Technical Reference