2. Electrode
2.1 Electrode/electrolyte interface
In an electrolyte, the charged species that make up the solute are homogeneously distributed in the solution, thus satisfying the principle of electroneutrality:
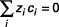 ( 56 )
( 56 )At equilibrium, the forces...
Exclusive to subscribers. 97% yet to be discovered!
You do not have access to this resource.
Click here to request your free trial access!
Already subscribed? Log in!

The Ultimate Scientific and Technical Reference
This article is included in
Conversion of electrical energy
This offer includes:
Knowledge Base
Updated and enriched with articles validated by our scientific committees
Services
A set of exclusive tools to complement the resources
Practical Path
Operational and didactic, to guarantee the acquisition of transversal skills
Doc & Quiz
Interactive articles with quizzes, for constructive reading
Electrode
Bibliography
Bibliography
Standards and norms
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) https://iupac.org/
Exclusive to subscribers. 97% yet to be discovered!
You do not have access to this resource.
Click here to request your free trial access!
Already subscribed? Log in!

The Ultimate Scientific and Technical Reference